Synthetic human-like fakes: Difference between revisions
Juho Kunsola (talk | contribs) (major reorg of the media) |
Juho Kunsola (talk | contribs) m (adjust heading levels) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Image 2 by Blanz and Vettel – Copyright ACM 1999 – http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311535.311556 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.]] | Image 2 by Blanz and Vettel – Copyright ACM 1999 – http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311535.311556 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.]] | ||
= Digital look-alikes = | == Digital look-alikes == | ||
{{#ev:vimeo|16292363|640px|right|''[[w:A Computer Animated Hand|A Computer Animated Hand]]'' is a 1972 short film by [[w:Edwin Catmull|Edwin Catmull]] and [[w:Fred Parke|Fred Parke]]. This was the first time that [[w:computer-generated imagery|computer-generated imagery]] was used in film to animate likenesses of moving human appearance.}} | {{#ev:vimeo|16292363|640px|right|''[[w:A Computer Animated Hand|A Computer Animated Hand]]'' is a 1972 short film by [[w:Edwin Catmull|Edwin Catmull]] and [[w:Fred Parke|Fred Parke]]. This was the first time that [[w:computer-generated imagery|computer-generated imagery]] was used in film to animate likenesses of moving human appearance.}} | ||
== Introduction to digital look-alikes == | === Introduction to digital look-alikes === | ||
[[File:The-diffuse-reflection-deducted-from-the-specular-reflection-Debevec-2000.png|thumb|right|260px|Subtraction of the diffuse reflection from the specular reflection yields the specular component of the model's reflectance. | [[File:The-diffuse-reflection-deducted-from-the-specular-reflection-Debevec-2000.png|thumb|right|260px|Subtraction of the diffuse reflection from the specular reflection yields the specular component of the model's reflectance. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{Q|Do you think that was [[w:Hugo Weaving|Hugo Weaving]]'s left cheekbone that [[w:Keanu Reeves|Keanu Reeves]] punched in with his right fist?|Trad|The Matrix Revolutions}} | {{Q|Do you think that was [[w:Hugo Weaving|Hugo Weaving]]'s left cheekbone that [[w:Keanu Reeves|Keanu Reeves]] punched in with his right fist?|Trad|The Matrix Revolutions}} | ||
== The problems with digital look-alikes == | === The problems with digital look-alikes === | ||
[[File:Deb-2000-reflectance-separation.png|thumb|360px|right|Image 1: Separating specular and diffuse reflected light | [[File:Deb-2000-reflectance-separation.png|thumb|360px|right|Image 1: Separating specular and diffuse reflected light | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
= Digital sound-alikes = | == Digital sound-alikes == | ||
Living people can defend¹ themselves against digital sound-alike by denying the things the digital sound-alike says if they are presented to the target, but dead people cannot. Digital sound-alikes offer criminals new disinformation attack vectors and wreak havoc on provability. | Living people can defend¹ themselves against digital sound-alike by denying the things the digital sound-alike says if they are presented to the target, but dead people cannot. Digital sound-alikes offer criminals new disinformation attack vectors and wreak havoc on provability. | ||
== Timeline of digital sound-alikes == | === Timeline of digital sound-alikes === | ||
* In '''2016''' [[w:Adobe Inc.]]'s [[w:Adobe Voco|Voco]], an unreleased prototype, was publicly demonstrated in 2016. ([https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I3l4XLZ59iw&t=5s View and listen to Adobe MAX 2016 presentation of Voco]) | * In '''2016''' [[w:Adobe Inc.]]'s [[w:Adobe Voco|Voco]], an unreleased prototype, was publicly demonstrated in 2016. ([https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I3l4XLZ59iw&t=5s View and listen to Adobe MAX 2016 presentation of Voco]) | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
== Examples of speech synthesis software not quite able to fool a human yet == | === Examples of speech synthesis software not quite able to fool a human yet === | ||
Some other contenders to create digital sound-alikes are though, as of 2019, their speech synthesis in most use scenarios does not yet fool a human because the results contain tell tale signs that give it away as a speech synthesizer. | Some other contenders to create digital sound-alikes are though, as of 2019, their speech synthesis in most use scenarios does not yet fool a human because the results contain tell tale signs that give it away as a speech synthesizer. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
== Documented digital sound-alike attacks == | === Documented digital sound-alike attacks === | ||
* [https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2019/09/04/an-artificial-intelligence-first-voice-mimicking-software-reportedly-used-major-theft/?noredirect=on 'An artificial-intelligence first: Voice-mimicking software reportedly used in a major theft'], a 2019 Washington Post article | * [https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2019/09/04/an-artificial-intelligence-first-voice-mimicking-software-reportedly-used-major-theft/?noredirect=on 'An artificial-intelligence first: Voice-mimicking software reportedly used in a major theft'], a 2019 Washington Post article | ||
---- | ---- | ||
== Example of a hypothetical digital sound-alike attack == | === Example of a hypothetical 4-victim digital sound-alike attack === | ||
A very simple example of a digital sound-alike attack is as follows: | A very simple example of a digital sound-alike attack is as follows: | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
== 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' 2018 by Google Research == | === Transclusion: 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' 2018 by Google Research === | ||
The Iframe below is transcluded from [https://google.github.io/tacotron/publications/speaker_adaptation/ 'Audio samples from "Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis"' at google.gituhub.io], the audio samples of a sound-like-anyone machine presented as at the 2018 [[w:NeurIPS]] conference by Google researchers. | The Iframe below is transcluded from [https://google.github.io/tacotron/publications/speaker_adaptation/ 'Audio samples from "Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis"' at google.gituhub.io], the audio samples of a sound-like-anyone machine presented as at the 2018 [[w:NeurIPS]] conference by Google researchers. | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
[[File:Spectrogram-19thC.png|thumb|right|640px|A [[w:spectrogram|spectrogram]] of a male voice saying 'nineteenth century']] | [[File:Spectrogram-19thC.png|thumb|right|640px|A [[w:spectrogram|spectrogram]] of a male voice saying 'nineteenth century']] | ||
= Footnotes = | == Footnotes == | ||
<references group="footnote" /> | <references group="footnote" /> | ||
= References = | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 2 June 2020
When the camera does not exist, but the subject being imaged with a simulation of a (movie) camera deceives the watcher to believe it is some living or dead person it is a digital look-alike.
When it cannot be determined by human testing whether some fake voice is a synthetic fake of some person's voice, or is it an actual recording made of that person's actual real voice, it is a digital sound-alike.

(1) Sculpting a morphable model to one single picture
(2) Produces 3D approximation
(4) Texture capture
(3) The 3D model is rendered back to the image with weight gain
(5) With weight loss
(6) Looking annoyed
(7) Forced to smile Image 2 by Blanz and Vettel – Copyright ACM 1999 – http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311535.311556 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.
Digital look-alikes
Introduction to digital look-alikes

Original picture by Debevec et al. - Copyright ACM 2000 https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311779.344855
In the cinemas we have seen digital look-alikes for over 15 years. These digital look-alikes have "clothing" (a simulation of clothing is not clothing) or "superhero costumes" and "superbaddie costumes", and they don't need to care about the laws of physics, let alone laws of physiology. It is generally accepted that digital look-alikes made their public debut in the sequels of The Matrix i.e. w:The Matrix Reloaded and w:The Matrix Revolutions released in 2003. It can be considered almost certain, that it was not possible to make these before the year 1999, as the final piece of the puzzle to make a (still) digital look-alike that passes human testing, the reflectance capture over the human face, was made for the first time in 1999 at the w:University of Southern California and was presented to the crème de la crème of the computer graphics field in their annual gathering SIGGRAPH 2000.[1]
“Do you think that was Hugo Weaving's left cheekbone that Keanu Reeves punched in with his right fist?”
The problems with digital look-alikes
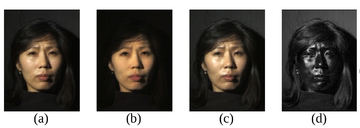
(a) Normal image in dot lighting
(b) Image of the diffuse reflection which is caught by placing a vertical polarizer in front of the light source and a horizontal in the front the camera
(c) Image of the highlight specular reflection which is caught by placing both polarizers vertically
(d) Subtraction of c from b, which yields the specular component
Images are scaled to seem to be the same luminosity.
Original image by Debevec et al. – Copyright ACM 2000 – https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311779.344855 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.
Extremely unfortunately for the humankind, organized criminal leagues, that posses the weapons capability of making believable looking synthetic pornography, are producing on industrial production pipelines synthetic terror porn[footnote 1] by animating digital look-alikes and distributing it in the murky Internet in exchange for money stacks that are getting thinner and thinner as time goes by.
These industrially produced pornographic delusions are causing great humane suffering, especially in their direct victims, but they are also tearing our communities and societies apart, sowing blind rage, perceptions of deepening chaos, feelings of powerlessness and provoke violence. This hate illustration increases and strengthens hate thinking, hate speech, hate crimes and tears our fragile social constructions apart and with time perverts humankind's view of humankind into an almost unrecognizable shape, unless we interfere with resolve.
For these reasons the bannable raw materials i.e. covert models, needed to produce this disinformation terror on the information-industrial production pipelines, should be prohibited by law in order to protect humans from arbitrary abuse by criminal parties.
Digital sound-alikes
Living people can defend¹ themselves against digital sound-alike by denying the things the digital sound-alike says if they are presented to the target, but dead people cannot. Digital sound-alikes offer criminals new disinformation attack vectors and wreak havoc on provability.
Timeline of digital sound-alikes
- In 2016 w:Adobe Inc.'s Voco, an unreleased prototype, was publicly demonstrated in 2016. (View and listen to Adobe MAX 2016 presentation of Voco)
- In 2016 w:DeepMind's w:WaveNet owned by w:Google also demonstrated ability to steal people's voices
- In 2018 Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems the work 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' (at arXiv.org) was presented. The pre-trained model is able to steal voices from a sample of only 5 seconds with almost convincing results
- As of 2019 Symantec research knows of 3 cases where digital sound-alike technology has been used for crimes.[2]
Examples of speech synthesis software not quite able to fool a human yet
Some other contenders to create digital sound-alikes are though, as of 2019, their speech synthesis in most use scenarios does not yet fool a human because the results contain tell tale signs that give it away as a speech synthesizer.
- Lyrebird.ai (listen)
- CandyVoice.com (test with your choice of text)
- Merlin, a w:neural network based speech synthesis system by the Centre for Speech Technology Research at the w:University of Edinburgh
Documented digital sound-alike attacks
- 'An artificial-intelligence first: Voice-mimicking software reportedly used in a major theft', a 2019 Washington Post article
Example of a hypothetical 4-victim digital sound-alike attack
A very simple example of a digital sound-alike attack is as follows:
Someone puts a digital sound-alike to call somebody's voicemail from an unknown number and to speak for example illegal threats. In this example there are at least two victims:
- Victim #1 - The person whose voice has been stolen into a covert model and a digital sound-alike made from it to frame them for crimes
- Victim #2 - The person to whom the illegal threat is presented in a recorded form by a digital sound-alike that deceptively sounds like victim #1
- Victim #3 - It could also be viewed that victim #3 is our law enforcement systems as they are put to chase after and interrogate the innocent victim #1
- Victim #4 - Our judiciary which prosecutes and possibly convicts the innocent victim #1.
Thus it is high time to act and to criminalize the covert modeling of human appearance and voice!
Footnote 1. Whether a suspect can defend against faked synthetic speech that sounds like him/her depends on how up-to-date the judiciary is. If no information and instructions about digital sound-alikes have been given to the judiciary, they likely will not believe the defense of denying that the recording is of the suspect's voice.
Transclusion: 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' 2018 by Google Research
The Iframe below is transcluded from 'Audio samples from "Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis"' at google.gituhub.io, the audio samples of a sound-like-anyone machine presented as at the 2018 w:NeurIPS conference by Google researchers.
The below video 'This AI Clones Your Voice After Listening for 5 Seconds' by '2 minute papers' describes the voice thieving machine presented by Google Research in NeurIPS 2018.

Footnotes
- ↑ It is terminologically more precise, more inclusive and more useful to talk about 'synthetic terror porn', if we want to talk about things with their real names, than 'synthetic rape porn', because also synthesizing recordings of consentual looking sex scenes can be terroristic in intent.
References
- ↑ Debevec, Paul (2000). "Acquiring the reflectance field of a human face". Proceedings of the 27th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH '00. ACM. pp. 145–156. doi:10.1145/344779.344855. ISBN 978-1581132083. Retrieved 2017-05-24.
- ↑ https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2019/09/04/an-artificial-intelligence-first-voice-mimicking-software-reportedly-used-major-theft/