Main Page
Welcome. This is a wiki about discovering ways of minimizing or stopping the damage from synthetic human-like fakes i.e digital look-alikes and clothed digital sound-alikes that result from covert modeling i.e. thieving of the human appearance and of the naked human voice and synthesis of malicious media.
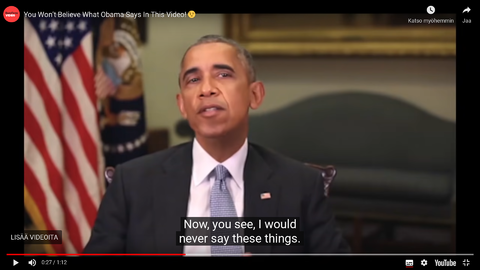
Click on the picture or Obama's appearance thieved - a public service announcement digital look-alike by Monkeypaw Productions and Buzzfeed to view an April 2018 public service announcement moving digital look-alike made to appear Obama-like. The video is accompanied with imitator sound-alike, and was made by w:Monkeypaw Productions (.com) in conjunction with w:BuzzFeed (.com). You can also View the same video at YouTube.com.[1]


In September 2019 w:Yle, the Finnish w:public broadcasting company, aired this result of experimental w:journalism, a facial digital look-alike of the President in office Sauli Niinistö, made with publicly available deepfakery tools, in its main news broadcast for the purpose of highlighting the advancing disinformation technology and problems that arise from it. Alternatively view film and Finnish language article on it at yle.fi
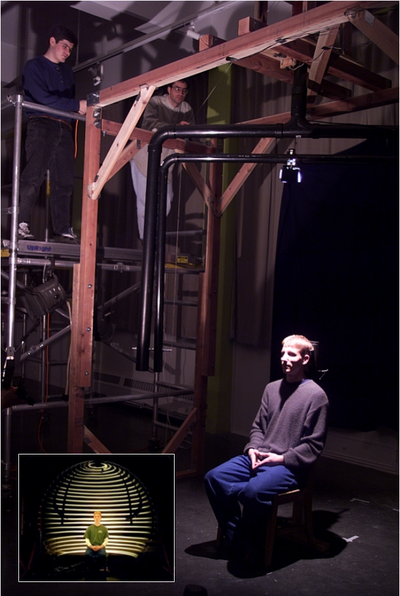

It consists of two w:rotary axes with w:height and w:radius control. A w:light source and a w:polarizer in front of the light source were placed on one arm and a camera and the other polarizer on the other arm. See picture below, for what they did to the captured reflection.
Original image by Debevec et al. – Copyright ACM 2000 – https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311779.344855 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.

(a) Normal image in dot lighting
(b) Image of the diffuse reflection which is caught by placing a vertical polarizer in front of the light source and a horizontal in the front the camera
(c) Image of the highlight specular reflection which is caught by placing both polarizers vertically
(d) The difference of c and b yields the specular highlight component
Images are scaled to seem to be the same luminosity.
Original image by Debevec et al. – Copyright ACM 2000 – https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=311779.344855 – Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page.
Join the struggle, demand Laws against synthesis and other related crimes from your legislators, support organizations, studies and events against synthetic human-like fakes and push for technological solutions and also cultural awkening.
SSFWIKI is an open w:non-profit w:copylefted w:public service announcement wiki that contains no pornography.
Anybody with a computer or a smartphone can edit this wiki anonymously after passing a CAPTCHA. Also free accounts are available upon reasonable request.
Definitions
When the camera does not exist, but the subject being imaged with a simulation of a (movie) camera deceives the watcher to believe it is some living or dead person it is a digital look-alike.
In 2017-2018 this started to be referred to as w:deepfake, even though altering video footage of humans with a computer with a deceiving effect is actually 20 yrs older than the name "deep fakes" or "deepfakes".[2][3]
When it cannot be determined by human testing or media forensics whether some fake voice is a synthetic fake of some person's voice, or is it an actual recording made of that person's actual real voice, it is a pre-recorded digital sound-alike. This is now commonly referred to as w:audio deepfake.
Real-time digital look-and-sound-alike in a video call was used to defraud a substantial amount of money in 2023.[4]
Introduction
Since the early 00's it has become (nearly) impossible to determine in still or moving pictures what is an image of a human, imaged with a (movie) camera and what on the other hand is a simulation of an image of a human imaged with a simulation of a camera. When there is no camera and the target being imaged with a simulation looks deceptively like some real human, dead or living, it is a digital look-alike.
Now in the late 2010's the equivalent thing is happening to our voices i.e. they can be stolen to some extent with the 2016 prototypes like w:Adobe Inc.'s w:Adobe Voco and w:Google's w:DeepMind w:WaveNet and made to say anything. When it is not possible to determine with human testing or testing with technological means what is a recording of some living or dead person's real voice and what is a simulation it is a digital sound-alike. 2018 saw the publication of Google Research's sound-like-anyone machine 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' at the w:NeurIPS conference and by the end of 2019 Symantec research had learned of 3 cases where digital sound-alike technology had been used for crimes.[5]
Then in 2018 at the w:Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) the work 'Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis' (at arXiv.org) was presented. The pre-trained model is able to steal voices from a sample of only 5 seconds with almost convincing results
The Iframe below is transcluded from 'Audio samples from "Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis"' at google.gituhub.io, the audio samples of a sound-like-anyone machine presented as at the 2018 w:NeurIPS conference by Google researchers.
Have a listen.
Observe how good the "VCTK p240" system is at deceiving to think that it is a person that is doing the talking.
Covert modeling poses growing threats to
- The right to be the only one that looks like me (compromised by digital look-alikes)
- The right to be the only one able to make recordings that sound like me (compromised by digital sound-alikes)
And these developments have various severe effects on the right to privacy, provability by audio and video evidence and deniability.
Therefore it is high time to act and to ban unauthorized synthetic pornography, build the Adequate Porn Watcher AI (concept) to protect humanity from visual synthetic filth and to criminalize covert modeling of the naked human voice and synthesis from a covert voice model!
Information about this wiki as of now
Currently it is week #10 and today is Tuesday 3 March 2026 and this wiki has 23 articles with 4,681 edits. 105 files have been uploaded. See more information about this wiki.
The domain ![]() stop-synthetic-filth.org is currently registered till Monday 2035-01-15 (check) and the registration will be extended as long as needed.
stop-synthetic-filth.org is currently registered till Monday 2035-01-15 (check) and the registration will be extended as long as needed.
Articles in this wiki
Brilliant stuff by others
- FacePinPoint.com was a countermeasure to non-consensual pornography in 2017-2021, invented by Lionel Hagege in 2015, that would protect humanity against the destructive effects of malicious synthetic pornography, if it were revived and purveyed as a public good.
- 'Detecting deep-fake audio through vocal tract reconstruction' is an epic scientific work, against fake human-like voices, from the w:University of Florida published in August 2022.
Stop Synthetic Filth! wiki original content
- Synthetic human-like fakes are sources of problems for humanity.
- Organizations, studies and events against synthetic human-like fakes lists organizations, events and services that have an aspect of being against the synthetic human-like fakes.
- Laws against synthesis and other related crimes is an ongoing effort to chart out what kind of laws exist, or are in the works or could exist to counter the problems.
- Help against appearance and voice theft is an ongoing effort to find help against problems of appearance and voice theft
- Adequate Porn Watcher AI (concept) #SSF! wiki proposed countermeasure to synthetic porn: Adequate Porn Watcher AI is a 2019 concept for an AI to protect the humans against synthetic filth attacks by looking for porn that should not be.
- Biblical connection - Revelation 13 and Daniel 7, wherein Daniel 7 and Revelation 13 we are warned of this age of industrial filth, is for those who believe in Jesus. We have a list of list of Bibles and churches if you want to join in studying and spreading the word against the beasts.
- Mediatheque | Glossary | Resources | Marketing against synthetic filth | Quotes | Atheist explanation | About this wiki | Scratchpad for quick drafting, sandbox if you want to try editing.
#SSF!'s predecessor domain ![]() Ban-Covert-Modeling.org #BCM! was registered on Thursday 2019-03-14. It will expire on Wednesday 2029-03-14 (check), unless renewed.
Ban-Covert-Modeling.org #BCM! was registered on Thursday 2019-03-14. It will expire on Wednesday 2029-03-14 (check), unless renewed.
Stop Synthetic Filth! in other languages in Wordpress
 Stop Synthetic Filth! wordpress in English #SSF! contains a contact form suited for anonymous use.
Stop Synthetic Filth! wordpress in English #SSF! contains a contact form suited for anonymous use. Arrêtons les saletés synthétiques! accueil en français #ASS! contient un formulaire de contact adapté à une utilisation anonyme
Arrêtons les saletés synthétiques! accueil en français #ASS! contient un formulaire de contact adapté à une utilisation anonyme Stoppi synteettiselle saastalle! kotisivu suomeksi #SSS! sisältää anonyymiin käyttöön sopivan yhteydenottolomakkeen
Stoppi synteettiselle saastalle! kotisivu suomeksi #SSS! sisältää anonyymiin käyttöön sopivan yhteydenottolomakkeen Stoppa syntetisk orenhet! hemsida på svenska #SSO! innehåller ett kontaktformulär som lämpar sig för anonym användning
Stoppa syntetisk orenhet! hemsida på svenska #SSO! innehåller ett kontaktformulär som lämpar sig för anonym användning Stopp sünteetisele saastale! koduleht eesti keeles #SSS! sisaldab anonüümseks kasutamiseks sobivat kontaktivormi
Stopp sünteetisele saastale! koduleht eesti keeles #SSS! sisaldab anonüümseks kasutamiseks sobivat kontaktivormi
Get in touch
- If you have any questions you can contact Juho Kunsola through the chat in the lower right hand corner, or the (anonymous) contact form at the SSF! wordpress or on wiki or alternatively leave a note on my my talk page (passing a CAPTCHA required). See my user page for a dedicated Whatsapp number if you would like to do that
- Stop Synthetic Filth is stop_synthetic_filth_org@d.consumium.org on diaspora*
- Stop-Synthetic-Filth.org wiki is tweeting as @stopsyntheticf on twitter
- Stop-Synthetic-Filth.org wiki has a page @stopsyntheticf on Facebook
- Stop Synthetic Filth! wiki - A call for resistance channel on YouTube.com
- @stopsyntheticf on Vimeo.com
Thank yous for free tech
-
.. but it has always helped w:Linux to be.
-
mw:MediaWiki is the medium of choice.
-
Served by w:Apache HTTP Server httpd.apache.org.
-
Choice of RDBMS is w:MariaDB, a fork back by the original people behind MySQL mariadb.org.
-
Run on copyleft w:Debian GNU/Linux Stable-branch servers debian.org. Debian also serves as Juho's everyday OS
-
w:Matomo (software) - Matomo.org is a free and open source w:web analytics application originating from w:New Zealand
-
LibreOffice (.org) by The Document Foundation (.org) is a versatile and well documented free office suite
References
- ↑
"You Won't Believe What Obama Says In This Video!". w:YouTube. w:BuzzFeed. 2018-04-17. Retrieved 2022-01-05.
We're entering an era in which our enemies can make anyone say anything at any point in time.
- ↑ Boháček, Matyáš; Farid, Hany (2022-11-23). "Protecting world leaders against deep fakes using facial, gestural, and vocal mannerisms". w:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 119 (48). doi:10.1073/pnas.221603511. Retrieved 2023-01-05.
- ↑ Bregler, Christoph; Covell, Michele; Slaney, Malcolm (1997-08-03). "Video Rewrite: Driving Visual Speech with Audio" (PDF). SIGGRAPH '97: Proceedings of the 24th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques: 353–360. doi:10.1145/258734.258880. Retrieved 2022-09-09.
- ↑ "'Deepfake' scam in China fans worries over AI-driven fraud". w:Reuters.com. w:Reuters. 2023-05-22. Retrieved 2023-06-05.
- ↑
Drew, Harwell (2020-04-16). "An artificial-intelligence first: Voice-mimicking software reportedly used in a major theft". w:washingtonpost.com. w:Washington Post. Retrieved 2021-01-23.
Thieves used voice-mimicking software to imitate a company executive’s speech and dupe his subordinate into sending hundreds of thousands of dollars to a secret account, the company’s insurer said